The connection between lipids ans aging
Lipids are natural compounds found in skin. While there are many kinds of lipids, ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids are the dominant forms.With age, lipid production declines. As a consequence, skin’s natural functions may become impaired, impacting barrier function and skin’s natural repair.
Appearance of accelerated aging due to lipid depletion
Roll over to learn more.
- Roughness
- Uncomfortable tightness
- Dullness
- Loss of facial fullness
Proven technology
First 2:4:2 cholesterol-dominant lipid correction
Triple Lipid Restore 2:4:2 is formulated with a maximized concentration of lipids: 2% pure ceramides, 4% natural cholesterol, and 2% fatty acids. This unique formulation utilizes an optimized concentration of ingredients to work synergistically on restoring skin’s external barrier, supporting natural self-repair, and nourishing skin for improvement in signs of accelerated aging.
Learn more>Correct
Nourish
2%
Pure
ceramides:4%
Natural
cholesterol:2%
Fatty
acids
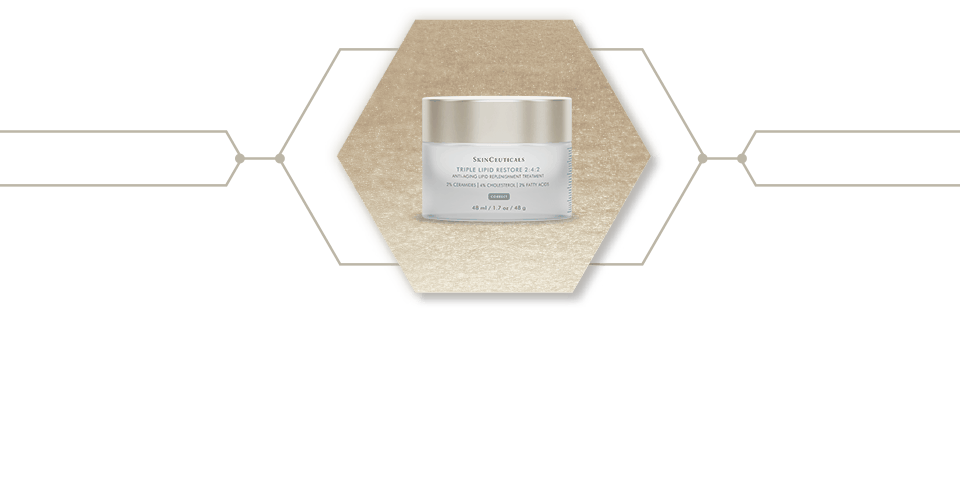

Triple lipid restore 2:4:2 visible results
Clinical improvement in signs of accelerated aging
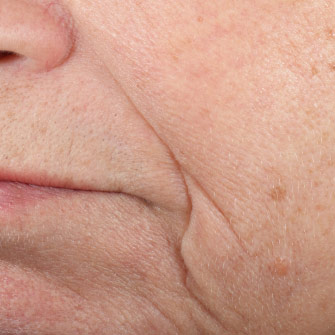
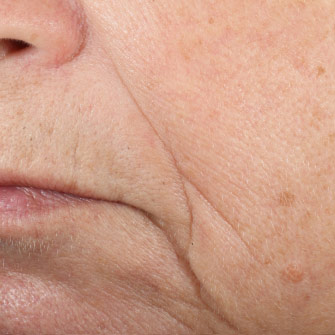
Average results for skin texture an laxity
- +66%
improvement in smoothness - +35%
improvement in laxity - +20%
improvement in evenness - +26%
improvement in radiance - +44%
improvement in pore appearance
Protocol: A dermatologist-controlled 8-week clinical study on 55 subjects with twice daily application of Triple Lipid Restore 2:4:2. Subjects also used SkinCeuticals Gentle Cleanser and Ultimate UV Defense SPF 30. Inclusion Criteria: Females ages 55-75 with moderate fine lines/wrinkles, uneven skin tone, skin dullness, skin roughness, lack of skin tone clarity, and lack of skin firmness.
Comprehensive regimen for anti-aging lipid correction
PreventAM
C E FERULIC®
Daytime antioxidant serum
delivers environmental protection,
while reducing the appearance of
fine lines and wrinkles
Learn more>
CorrectAM + PM
TRIPLE LIPID RESTORE 2:4:2
Anti-aging treatment refills cellular lipids
to support natural repair and nourishment
Learn more>